Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Vladimir Putin recently held bilateral talks at the 23rd India-Russia Annual Summit, where they established an expansive canvas of energy and trade collaborations stretching to 2030. PM Modi described the India-Russia friendship as a "pole star" (dhruva tara), highlighting its certainty and sustained, long-term significance despite global challenges and crises.
🌐 Strategic Partnership: A New Era of Cooperation

The leaders emphasized their shared independent foreign policy calling for a "more just, democratic multipolar world order and respect for sovereignty". This bilateral meeting marks a significant strengthening of ties between the two nations, with commitments spanning multiple strategic sectors.
Key Summit Outcomes:
- Nuclear Energy Cooperation: Lifecycle and fuel cycle support for Kudankulam nuclear power plant
- Arctic Engagement: Regular bilateral consultations on Arctic-related issues and Northern Sea Route cooperation
- Trade Expansion: $100 billion bilateral trade target by 2030
- Space Partnership: Enhanced ISRO-Roscosmos collaboration on peaceful uses of outer space
- Labour Mobility: 16 MoUs signed covering diverse sectors
- Currency Settlement: Reduced dependence on U.S. dollar through national currency transactions
⚛️ Expanding Nuclear and Space Cooperation
Nuclear Energy: A Pillar of Strategic Alliance
Cooperation in the nuclear energy sector is set to broaden significantly. The nations committed to lifecycle and fuel cycle support for the operation of the Kudankulam nuclear power plant. Furthermore, they are focused on constructing the remaining nuclear power units at the Kudankulam site, including finalizing timelines for fuel and equipment supplies.
🔬 Future Nuclear Developments:
India to "strive to" allot a second site for a nuclear plant, which will be subject to "further discussion". Both sides also agreed to accelerate technical and commercial discussions concerning the Russian VVER (Vodo-Vodyanoi Energetichesky Reaktor) nuclear reactors for joint development, research, and design of nuclear plants.
Notable: President Putin announced Russia's willingness to collaborate with India on small modular nuclear reactors—a frontier technology for future energy needs.
Space Cooperation: Reaching for the Stars
In the space sector, both countries welcomed the "enhanced partnership" between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Russian state-owned corporation Roscosmos, focused on the peaceful use of outer space.
🏔️ Arctic Engagement: India's Northern Frontier
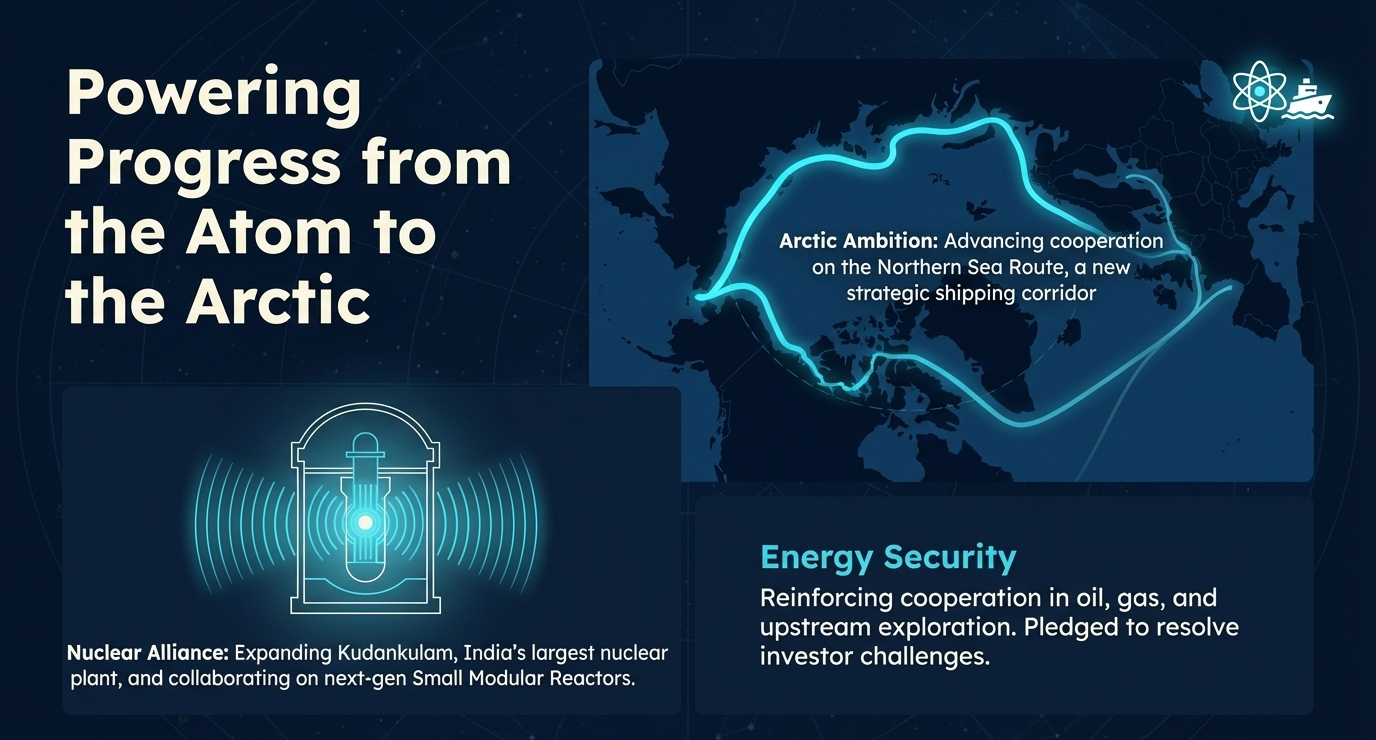
India and Russia have committed to holding "regular bilateral consultations" on Arctic-related issues. The leaders also welcomed the progress achieved in multi-faceted bilateral cooperation concerning the Northern Sea route.
This Arctic engagement signals India's strategic pivot toward maintaining presence and influence in emerging geopolitical hotspots, particularly as climate change opens new maritime routes.
💰 Trade, Energy Security, and National Currency Settlement
Energy Security: The Vital Pillar
Energy security remains a "strong and vital pillar of the India-Russia partnership". The joint statement included extensive references to energy security, noting current and potential cooperation in areas like:
Energy Cooperation Areas:
- Oil and oil products
- Oil refining and petrochemical technologies
- Upstream technologies
- Joint resolution of investor challenges in the energy sector
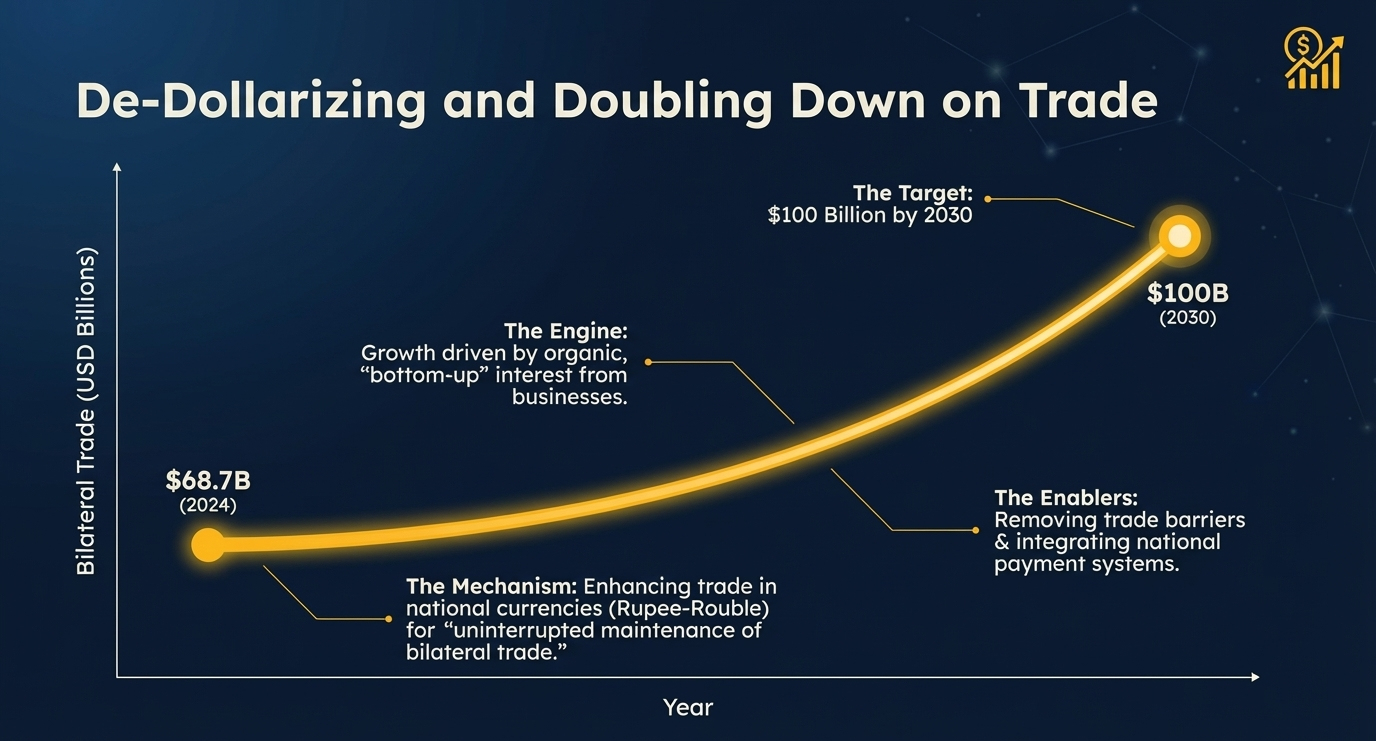
Trade Revolution: De-dollarization Strategy
A major focus of the summit was boosting trade using national currencies. India and Russia agreed to continue working towards enhancing the settlement of bilateral trade in their respective national currencies.
⚠️ Geopolitical Significance:
This move is designed to reduce the countries' dependence on the U.S. dollar and help address India's widening trade deficit with Russia. This de-dollarization strategy reflects broader geopolitical realignment, positioning India and Russia as independent economic actors.
To ensure uninterrupted maintenance of bilateral trade, the countries will continue jointly developing systems of bilateral settlements. They also agreed to consult on enabling the interoperability of national payment systems, financial messaging systems, and central bank digital currency platforms.
Trade Target: $100 Billion by 2030
The two leaders discussed removing tariff and non-tariff barriers to achieve their revised bilateral trade target of $100 billion by 2030.
Elements for Achieving $100B Trade Target:
- Addressing tariff barriers
- Removing non-tariff trade barriers
- Eliminating logistical bottlenecks
- Ensuring smooth payment mechanisms
- Finding mutually acceptable solutions for insurance and reinsurance issues
👥 Labour Mobility and People-to-People Ties
Worker Exchange Program

The two sides signed sixteen MoUs covering diverse fields, including semi-skilled workers, fertilizers, media, and academic collaboration.
India and Russia signed two agreements aimed at enhancing the mobility of Indian skilled and semi-skilled workers to Russia. Official sources indicated that Russia has a reported demand for half a million semi-skilled workers.
One agreement specifically addresses the "Temporary labour activity of citizens of one state in the territory of the other state"—formalizing what was previously an informal arrangement vulnerable to exploitation.
Tourism and Cultural Exchange
To enhance people-to-people contacts, PM Modi announced the reciprocal gratis grant of 30-day e-tourist visas and the gratis grant of group tourist visas to Russian nationals. These visa facilitations are designed to strengthen cultural and social bonds between the two nations.
New media collaboration was also marked with the launch of the Indian edition of the Russian state English broadcaster Russia Today—expanding information and cultural reach.
🕊️ India's Position on Ukraine: Advocacy for Peace
Regarding the conflict in Ukraine, Prime Minister Modi reiterated India's consistent position, which advocates for peace. Mr. Modi called for a peaceful solution and stated that India "has always been, and will always be ready to contribute," welcoming all efforts being made for a peaceful and lasting resolution.
India's Diplomatic Stance: India maintains its principled position of neutrality on the Ukraine conflict while expressing readiness to facilitate peace efforts. This balanced approach reflects India's broader foreign policy commitment to sovereignty, international law, and peaceful resolution of disputes.
📊 Summary: Key Takeaways from the 23rd India-Russia Summit
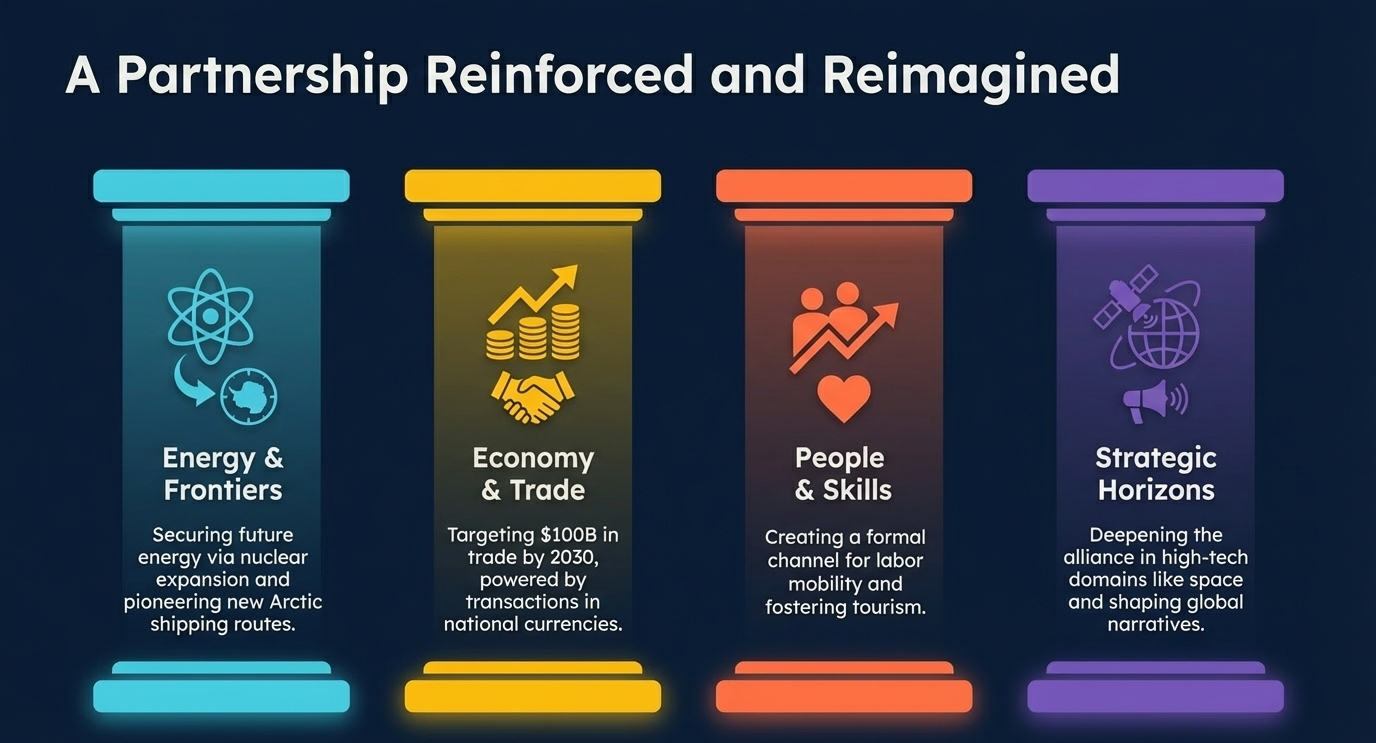
| Sector | Key Commitment | Timeline/Target |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear Energy | Lifecycle support, Kudankulam expansion, VVER reactors, small modular reactors | Ongoing + Future |
| Space | Enhanced ISRO-Roscosmos partnership for peaceful use of outer space | Ongoing |
| Arctic | Regular consultations, Northern Sea Route cooperation | Ongoing |
| Trade | De-dollarization, tariff removal, logistical improvements | $100B by 2030 |
| Labour | Formal mobility agreements for semi-skilled workers | Immediate |
| Culture | E-visa facilitation, media collaboration (Russia Today) | Immediate |
Strategic Implications
This summit reinforces India-Russia as a multivariate strategic partnership covering nuclear energy, space, Arctic engagement, trade de-dollarization, and labour mobility. The $100 billion trade target and enhanced cooperation frameworks signal a long-term commitment to bilateral relations, positioning both nations as independent actors in a multipolar world.